

| <<= Back | <<= Computer Classes | Next =>> |
In this lesson you will learn:This lesson shows where and demonstrates how Windows settings can be changed. This information is for use on your home and business computers. The Lab Computers will not allow changes to be made that affect the operating system. This information is for instructional purposes only. So you accidentally deleted a file and you now you want it back. Fortunately Windows Recycle Bin protects you - to a point. NOTE: To begin this lesson, place a Text 1.txt document into your personal folder in My Documents / Personal, and then right click it and DELETE IT. If it is not in recycle bin then go back to the deleting Folders class and see what happened. Hint: "My Documents" Recycle BinThe Windows Operating System holds files in a special folder called Recycle Bin until a disk clean-up utility runs and cleans out the files, or until you restore them or delete them permanently. Open Recycle Bin through Windows Explorer or double click the icon on your desktop. Open up the left pane (Click on the 'Folders' button) and you will find it at the bottom of the left pane. Click on View >> Details. 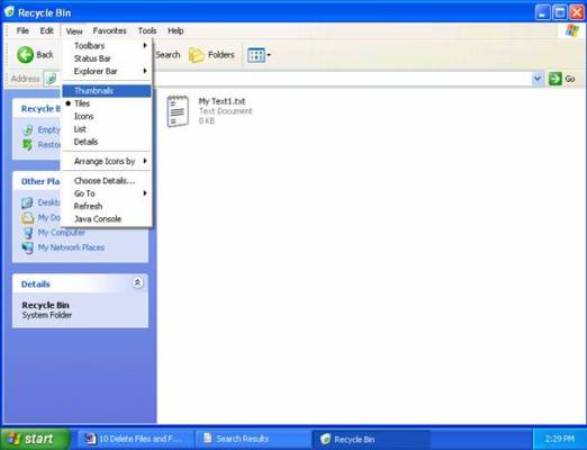
Choosing 'View' from the menu allows you to change the way files are displayed or to re-arrange the order of the files. Click a few of the options to see the changes, then click on 'View >> Details when you are ready to continue. 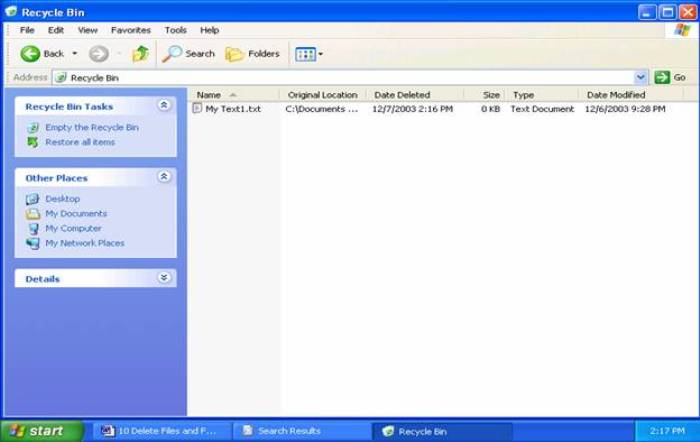
Your files should show details similar to this: Multiple files will be listed down the Right pane The Recycle Bin window has a menu bar with many of the familiar options. In 'Details' view, you can also click the buttons above each column, as in other windows, and sort the list by size, type, date deleted etc. If part of the list is obscured because the column is not wide enough, maximize the window or point to the left or right side of the column button and then double click or drag when the pointer changes to a double-headed arrow. 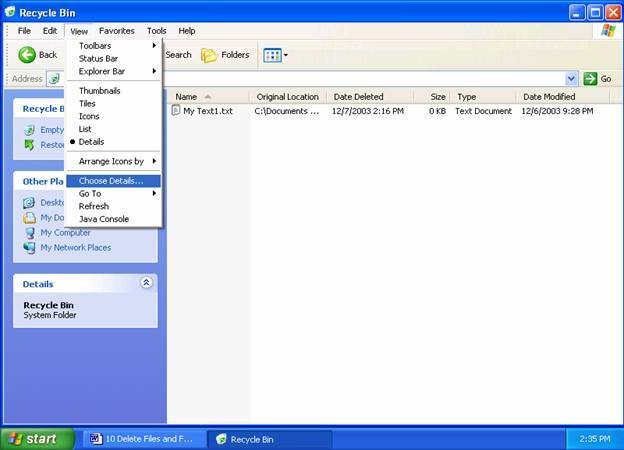
The column headings (Name, Size, Type etc.) can be turned on or off to suit your preferences. When Recycle Bin is opened, there are options of either permanently deleting the files or restoring the files to their original locations. The location that it will be restored to is shown in the 'Original Location'. 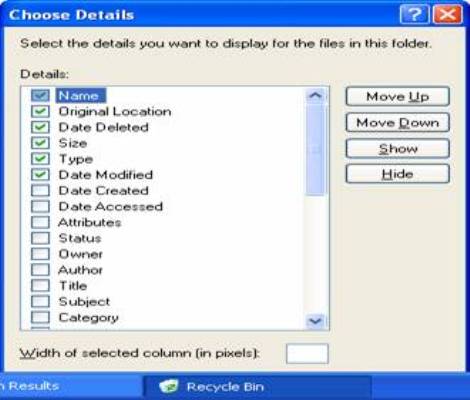
File Recovery: Where'd it go?Double Click the Recycle Bin to open it and view its contents. You may find that it needs to be made larger to see more files. To recover a file, simply click it and select File >> Restore, or right click it and select 'Restore'. The file is then restored to its original location. The Recycle Bin is a large queue with the recently deleted files listed at the top. The oldest files in the queue are automatically deleted when the queue becomes full. As long as the Recycle Bin is big enough (and you can change this), there is a good chance that you can recover even your oldest files days or weeks after they've been deleted. BUT, be careful when you delete files and folders, because some deletions will occur without sending them to the Recycle Bin. This was covered in the Deleting Files class.Instead of using Menu options, you can use drag and drop techniques. You can delete files by dragging them into the Recycle Bin, and you can recover by dragging them back out. However, the original folder for the deleted files won't be restored if you drag and drop files into other folders to restore them. To move the file to another location simply drag and drop it where you need it. Recovering a File or FolderWhen you delete a folder from hard drives on the computer its entire contents, including all sub-folders go to the Recycle Bin. But you do not see the folders and sub-folders themselves in the queue window - just the folder and file names. The folders' names are still connected with the files in the Recycle Bin: you can see them listed in 'Original Location' next to each file that was deleted. The 'Original Location' becomes the location that it will be restored TO. If you restore a file by selecting File> Restore (not by dragging it out into a new folder), the file will return to its original Folder, as identified under Original Location. If the file and its folder were deleted together, the folder will be restored ALONG WITH the file. Cleaning Out the Recycle BinTo clear out the Recycle Bin, choose File > Empty Recycle Bin. You can also delete individual files by selecting them and choosing File >> Delete. This permanently deletes the files without any chance of recovery. Unless someone is using a special recovery utility designed specifically for the purpose, the only way to recover files or folders is by restoring them from a back up disk. Oh, you didn't back up your files? Now you know why backups are considered to be essential business practices. Making the Recycle Bin Larger or SmallerThe Recycle Bin has a limited amount of disk space to use for your deleted items, so if you delete a large folder that has a lot of files, and it will not fit into the queue, the files will be deleted permanently. If you use up the available space, you will not be able to recover some files unless the proper settings are made To change the amount of disk space set aside for the Recycle Bin for deleted objects, close the window and right click on Recycle Bin on the right pane of Windows Explorer and then choose 'Properties'. Recycle Bin can be set up so that each drive requires space for deleted files. You can customize individual drives by clicking the tab for that drive. You can configure default settings for all drives using the Global (General) Tab. Using the slider, space can be allocated in % of the total drive space. Increasing this REDUCES the amount of free space left on the disk for other files to be stored. In the event of 'Disk Full' errors on copying files this is the FIRST PLACE to look. 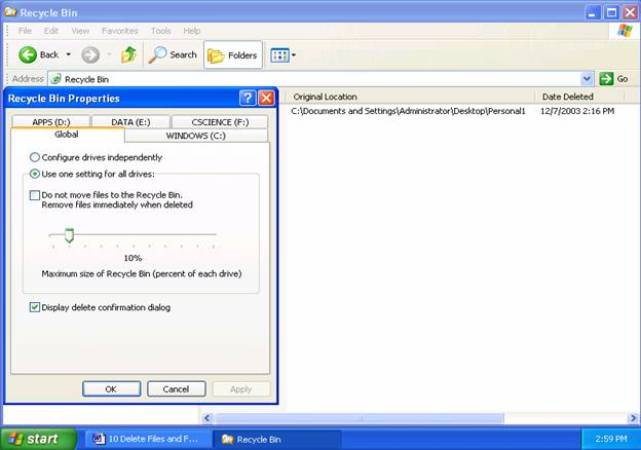
The Recycle Bin can be set up so that each drive requires space for deleted files Recycle Bin PropertiesAs a general rule you, as a home PC user, would never need to change these settings. A technician would have to change them for certain situations, and if there was trouble, this is the first place they would look, in case a user changed something here.
This would be considered quite adequate for most users. You can decrease this value if you are running out of disk space, or increase it if you have a lot of disk space and want to make sure you can recover more files. Deleting folders and Files permanently without any warning is probably a bad idea! Best leave this for the Technicians that know how to use it This is always checked by default, but warnings can be removed for automatic file operations that will stop if warnings are turned on. If there are no automatic processes or programs handling your files for you, it is best to always have this turned on. Techie stuff The settings you make on the Global Tab determine the settings for all drives unless you click 'Configure drives independently'. To configure individual drives click the tab for that drive. Use this with caution. The Individual drive setting 'locks' the drive space on each of the drives and makes that space unusable for anything else. Separate permissions can be designated for each drive, but doing so can make automated maintenance and disk cleanup utilities fail. Reminder: If you delete files from a USB Drive or a floppy disk or the desktop, they may not appear in the Recycle Bin. Windows will ask you to verify the deletion only once and the deletion will be final. If the folder or file is too big to fit in the Recycle Bin, it will be deleted permanently. You may or may not be notified first, depending on some other conditions, like attributes and size etc. |
NOTE: These are posted for student and staff educational & class use.